Brief introduction of vacuum coating method for inner wall of tube
The introduction
Electroplating was the earliest method to treat the inner surface of the tube, but the electrolyte polluted the environment. Later, vacuum Deposition was adopted to treat the inner surface of tubular components, including Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Chemical vapor deposition
The medium used by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method is gas, which is not limited by the shape and size of the inner cavity. As long as the tubular component is immersed in the working gas, the required film can be deposited on the inner surface, so it is easier to deal with the workpiece of complex shape.
1) Thermochemical vapor deposition (H-CVD) method
In the 1990s Kwatera designed a CVD device with a coated inner surface, as shown in Figure 1. The device is composed of quartz tubes to form a tubular vacuum chamber. The plated tubular members are placed in the vacuum chamber and can rotate along the axial direction of the vacuum chamber. Si3N4 film is deposited on the surface of the quartz tube with an inner diameter of 30 mm through a mixture of gas containing silane, nitrogen, ammonia and argon.
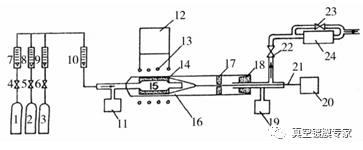
1 -- Argon cylinder; 2 - ammonia cylinder; 3 -- N2 containing 3% SiH4; 4,5,6 - cylinder switch; 7,8,9,10 - flow meter; 11 -- barometer; 12 - high frequency induction generator; 13 - high frequency induction generator core; 14 - graphite heater; 15 - tube to be coated; 16 -- columnar quartz reactor; 17 - graphite bearing rod; 18 - rubber bottle stopper; 19 -- barometer; 20 - motor; 21 - rotary heater rod; 22,23 - cylinder switch;
FIG. 1 Device for CVD deposition of Si3N4 film in the tube
2) Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method
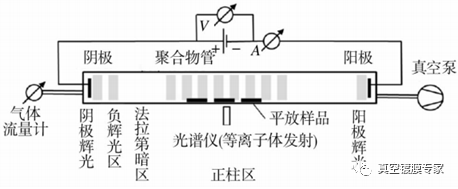
Lackner et al. used a pulsed DC glow discharge device (as shown in Figure 2) to deposit DLC films on the inner wall of the polymer tube. It was found that different gases (argon, oxygen, acetylene and air) had a great influence on the wettability of DLC films deposited and bombarded by the inner wall.
FIG. 2 Low pressure pulse DC glow discharge device
Physical vapor deposition
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technology refers to that the surface of material source (solid or liquid) is vaporized into gaseous atoms or molecules or partially ionized into ions by Physical means under vacuum condition and through the process of low pressure gas (or plasma). The technique of depositing a thin film with a specific function on the surface of a substrate.
1) Vacuum evaporation method
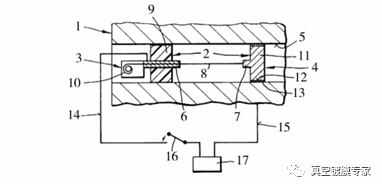
Helmut Neff et al. from Germany set up a linear metal target in the tube and deposited a metal film in the weapon tube by applying a pulse current on the target to make it discharge and evaporate, as shown in Figure 3.
1 - weapon tube; 2 - support frame; 3 - electrode 1; 4-2 electrode; 5 - the inner surface of the weapon; 6 -- main electrode 1; 7 -- main electrode 2; 8 - linear target; 9 - insulation parts; 10 -- target volume; 11 - metal block; 12 - metal block periphery; 13 - auxiliary electrode; 14 - wire 1; 15 - wire 2; 16 - switch; 17 - pulse power supply;
FIG. 3 Schematic diagram of evaporating gold-plated film device in tube
2) sputtering coating method
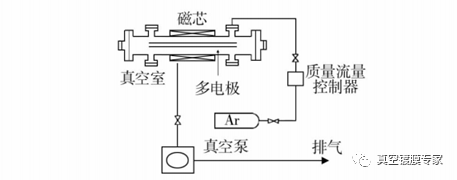
Kawasaki in Japan invented a magneto-controlled hollow cathode discharge device, as shown in Figure 4. The device is used to deposit titanium film in the copper tube, the inner diameter of the copper tube is 20 mm, 100 mm long. Argon plasma is generated through a DC power source. Because the magnetic core is set outside the tube fitting to be processed to generate magnetic field, the plasma flow generated by the hollow cathode discharge is controlled and controlled, which promotes the axial uniformity of the film in the tube to a certain extent.FIG. 4 Magnetically controlled hollow - cathode discharge device
3) Arc ion plating technology
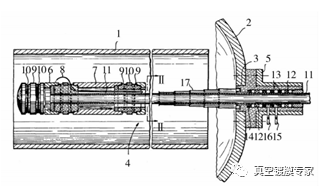
Wesemeyer et al. in Germany developed a center column target arc ion coating device, as shown in FIG. 5, and obtained a US patent. The device can coating the inner surface of the pipe with an inner diameter of 100 mm, but cannot handle the pipe with an inner diameter of less than 100 mm due to the size limitation of the column target.
1, pipe fittings; 2 - vacuum chamber; 3 - vacuum chamber opening; 4 - arc evaporation device; 5 - sealing ring; 6 - cathode; 7 - anode; 8 - arc needle; 9 - soft magnet; 10 - locking device; 11 - lever; 12 - ball bearing; 13 - gasket; 14 - dustproof pad; 15 - pre-suction port; 16 - fine suction mouth; 17 - telescopic shielding structure
FIG. 5 Target arc ion coating device for center column on inner surface
summary
In recent years, the demand for inner surface protection of tube workpiece is higher and higher, which also promotes the continuous improvement and development of related technology. Electroplating technology will be phased out due to environmental pollution. At present, among chemical vapor deposition methods, thermochemical vapor deposition (H-CVD) method and PECVD method can use organic gas to split and ionize the coating in the tube. A wide variety of films can be deposited by magnetron sputtering method, but it is limited by the length and shape of the central cylindrical target. The arc ion plating technology can get a relatively dense film on the inner surface of the pipe fitting. Due to the loss in the process of plasma transmission and the pollution of large particles, the coating on the inner surface of the thinner and longer pipe fitting still faces great challenges. In general, various inner surface vacuum coating technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages. How to find a suitable and more reliable inner surface coating technology is still the focus of future research.
 18922924269
18922924269
