How to control and optimize vacuum coating parameters to achieve better results
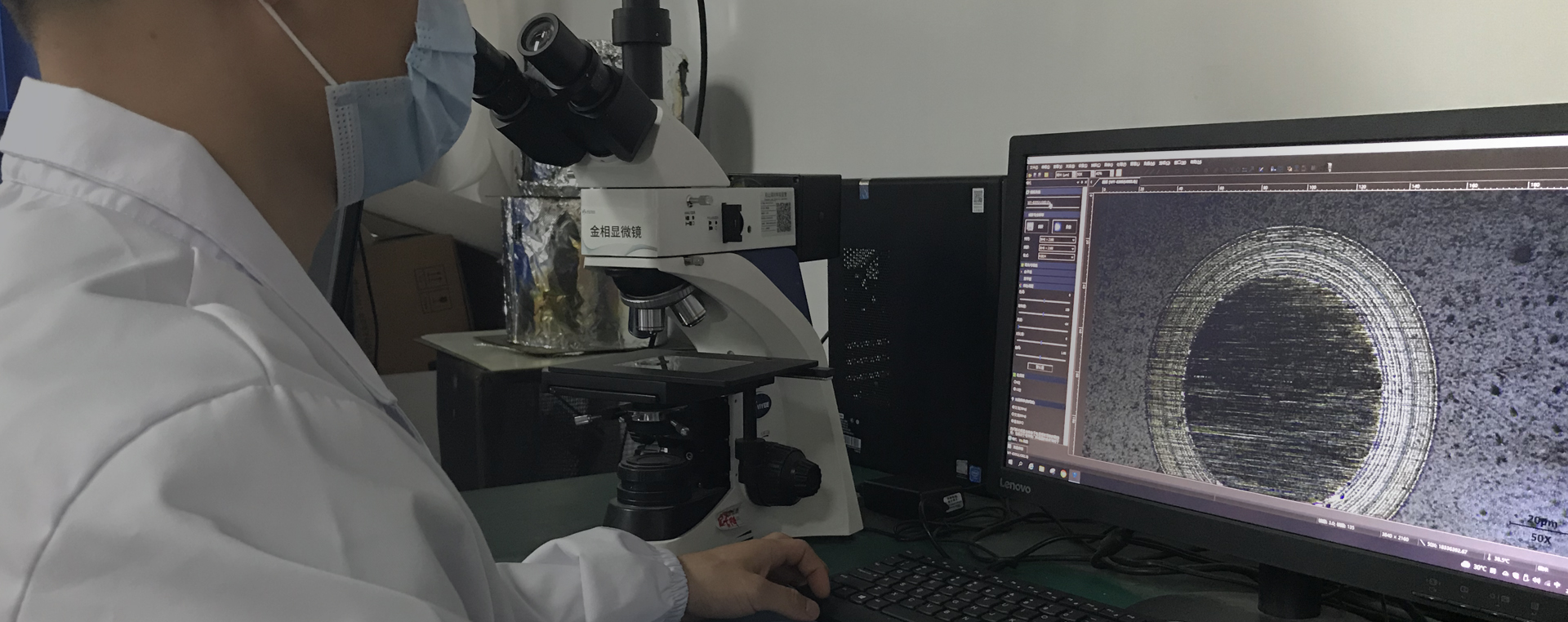
The temperature of the evaporation source is a key parameter.For different coating materials,there are specific evaporation temperature ranges.If aluminum metal is evaporated,the temperature is generally between 1200-1400℃.
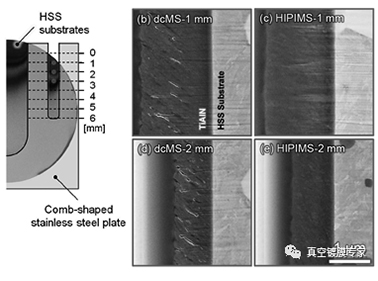
How to control the microstructure of thin films during the deposition process using HIPiMS technology
HIPiMS technology can effectively regulate the microstructure of thin films during the deposition process by controlling a series of process parameters. These parameters include but are not limited to power, pulse frequency, gas pressure, substrate temperature, etc. The following is a detailed explanation:
Can HiPIMS power supply deposit oxides
HiPIMS (High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering) is a thin film deposition technique that utilizes high-density plasma generated by a high-frequency pulse power source for material sputtering deposition.
Difference between vacuum coating and electroplating
Vacuum coating and electroplating, as two common surface treatment technologies, differ significantly in a number of ways. The following is a detailed description of the differences between the two:
Vacuum deposition process flow
Vacuum deposition is a common surface treatment process, which is often used to manufacture optical lenses, solar panels, LED and other products. The main process includes the following steps:
DLC coating - \"plain clothes\" for automobile wiper
Wiper is an important device of automobile, which plays a vital role in safe driving.
A good wiper must have the characteristics of heat resistance, cold resistance, acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, can fit the windshield, reduce the burden of the motor,
Study on plasma permeability of porous ceramic materials
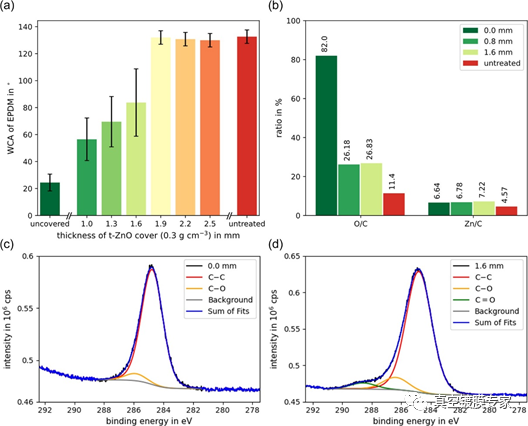
Zinc oxide (ZnO), as a high band gap semiconductor, has been widely used in gas sensing and catalysis fields due to its excellent chemical stability and biocompatibility, especially t-ZnO with three-dimensional porous skeleton structure.
 0769-81001639
0769-81001639